Aug
A Step-by-Step Guide to AWS Cloud Migration

Migrating to the cloud has become more than just a trend—it is now a necessity for businesses aiming to innovate, scale, and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Amazon Web Services (AWS), recognized as one of the most reliable and feature-rich cloud providers, offers a comprehensive suite of tools and services that enable smooth and secure transitions. For organizations considering cloud migration to AWS requires strategic planning, thorough assessment, and precise execution to minimize disruption and ensure long-term success.
This detailed guide outlines the AWS cloud migration process in comprehensive steps, helping organizations of all sizes make a seamless and successful shift to the AWS cloud platform.
Step 1: Assess Your Existing Infrastructure
The first step in any AWS cloud migration is gaining a clear understanding of your current IT landscape, including application performance, resource usage, and any interdependencies that affect operations.
- Applications and workloads in use: Identify all active applications and workloads running across your infrastructure. Document their purposes, resource consumption, usage patterns, and whether they are cloud-compatible or require modification before migration.
- Servers, databases, and storage resources: Take inventory of your physical and virtual servers, databases, and storage systems. Understand current configurations, capacity, data volumes, and performance to evaluate readiness and scalability in the cloud.
- Interdependencies between systems and services: Map out how systems, applications, and services are connected. Knowing interdependencies ensures smoother transitions by avoiding disruptions and preserving communication between components during and after migration.
- Performance and latency requirements: Determine the performance benchmarks and latency sensitivity of each application. This will help in selecting suitable AWS services and instance types that align with your operational expectations and user experience.
- Security configurations and compliance obligations: Review current security measures, access controls, and data protection practices. Identify industry compliance needs (like GDPR or HIPAA) to ensure your AWS environment meets regulatory and corporate security standards.
Start by categorizing applications based on criticality and complexity. Determine which applications can be moved easily, which require significant rework, and which are best retired or replaced. AWS provides tools such as the Migration Readiness Assessment (MRA), which helps organizations evaluate their preparedness for migration and identify gaps in skills, tools, governance, and security.
This stage is also where business objectives must be clearly defined. Are you aiming to reduce capital expenditure? Improve application performance and availability? Increase scalability or enhance data security? Clarifying these goals early on will inform decision-making throughout the AWS cloud migration journey.
Step 2: Define Your Migration Strategy
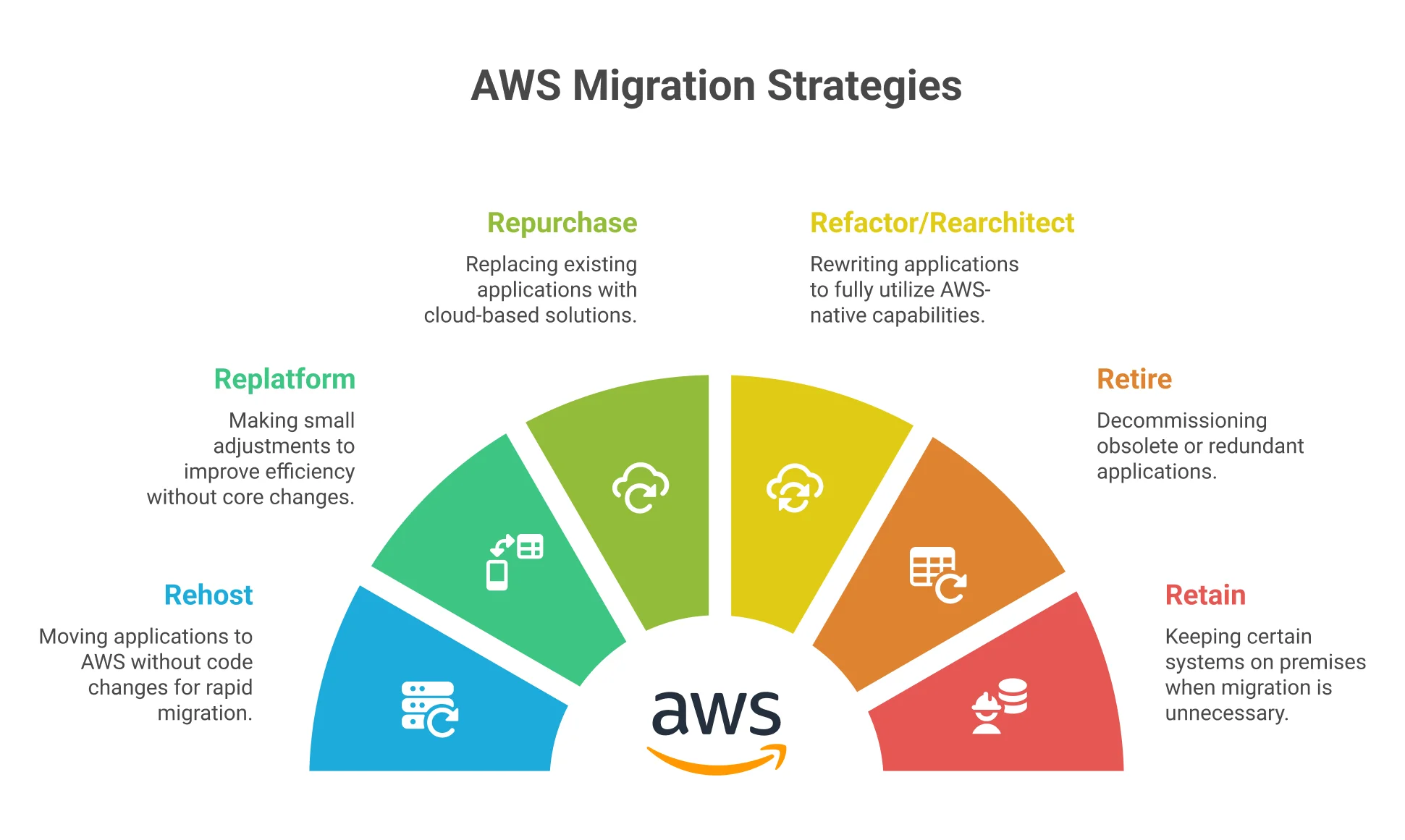
Once you have assessed your infrastructure, the next step is to determine the migration strategy that best suits your business needs. AWS promotes six primary strategies, known as the “6 R’s”:
- Rehost (Lift and Shift): This approach involves moving applications to AWS with no code changes, making it ideal for rapid migrations. It’s commonly used to quickly transition legacy systems without altering architecture or requiring application-level modifications.
- Replatform: Replatforming makes small adjustments to improve efficiency without changing the application’s core functionality. An example includes moving from self-hosted databases to AWS-managed services like RDS while keeping the application logic mostly intact.
- Repurchase: This strategy replaces existing applications with cloud-based solutions. For instance, shifting from an in-house CRM to a SaaS solution like Salesforce. It’s effective when existing tools are outdated or costly to maintain.
- Refactor/Re-architect: This involves reimagining and rewriting applications to fully utilize AWS-native capabilities like microservices, containers, or serverless. Ideal for modernizing applications to achieve scalability, agility, and long-term cloud efficiency.
- Retire: During assessment, you may find obsolete or redundant applications. The retire strategy involves decommissioning such systems, which reduces cost, simplifies architecture, and frees up IT resources for more critical cloud-ready workloads.
- Retain: Not all applications need to move to the cloud. The retain strategy keeps certain systems on premises when migration is unnecessary, cost-prohibitive, or if they require specialized hardware or meet specific regulatory conditions.
Each application in your ecosystem may require a different approach. Legacy systems with minimal change might be rehosted, while customer-facing apps needing scalability and rapid innovation may benefit from complete refactoring or re-architecting.
Step 3: Create a Detailed Migration Plan
A well-structured migration plan is critical for success. It should be created collaboratively, involving stakeholders from IT, security, operations, finance, and business units to ensure alignment with organizational goals and minimal disruption during the transition.
- A realistic timeline with milestones: Establish a clear migration timeline with achievable milestones for each phase. Include preparation, testing, and post-migration periods to keep progress on track and allow flexibility for adjustments as challenges arise.
- Roles and responsibilities for all team members: Define specific roles and responsibilities for every team member involved in the migration. Clarity ensures accountability, minimizes overlap, and keeps all parties aligned and informed throughout the migration process.
- Budget estimates and approval processes: Prepare detailed cost projections that account for cloud infrastructure, tools, labor, and unexpected contingencies. Outline the necessary steps for securing budget approvals to avoid delays and ensure financial alignment across departments.
- A comprehensive communication strategy: Develop a structured communication plan to keep all stakeholders updated on progress, timelines, changes, and issues. Clear internal inside communication helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that all teams are working with accurate information.
- Risk assessments and contingency plans: Identify potential risks such as downtime, data loss, or security breaches. Prepare mitigation strategies and contingency plans to handle unexpected events and maintain business continuity during each phase of the migration.
- Validation and rollback procedures: Establish thorough validation protocols to verify system integrity post-migration. Include rollback procedures in case of failures, allowing systems to revert safely and quickly to a stable state without data loss or disruption.
Organizations often benefit from a phased migration approach, starting with less critical systems or proof-of-concept (PoC) environments. This allows teams to familiarize themselves with AWS services and tooling, and to validate their migration processes before moving mission-critical workloads.
AWS’s Migration Acceleration Program (MAP) is also available to support organizations with large-scale AWS cloud migration. It offers technical expertise, tools, training, and even financial incentives to reduce the cost and complexity of migration. If you’re unsure whether your organization qualifies for AWS MAP, feel free to contact us for guidance and a tailored migration plan.
Step 4: Choose the Right AWS Tools and Services
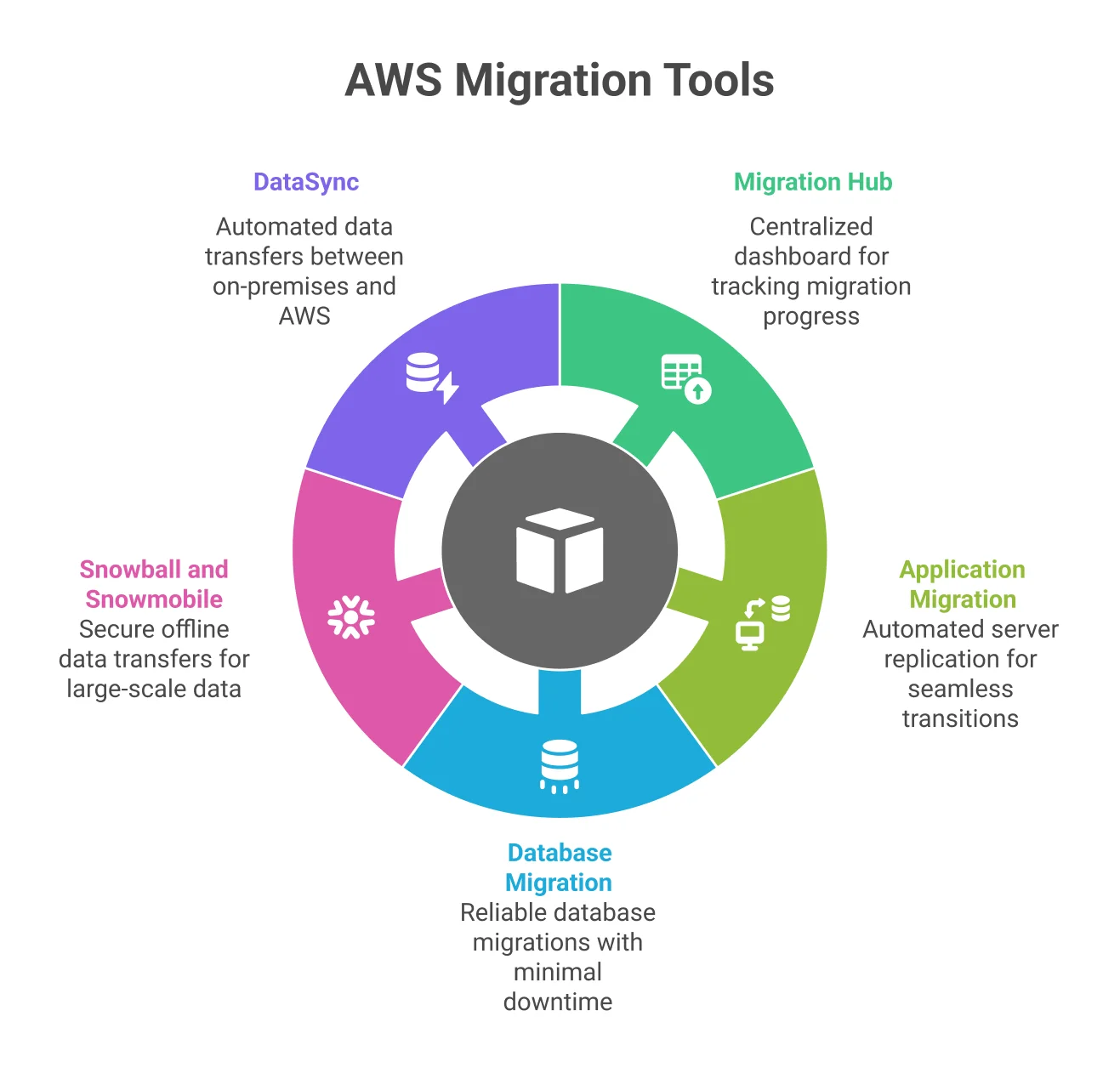
Selecting the appropriate AWS tools can significantly streamline the AWS cloud migration process. At this stage, it is important to align your migration goals with technologies that support scalability, security, and long-term performance. AWS offers a comprehensive suite of solutions tailored specifically for cloud migration. These tools form the backbone of effective AWS cloud migration:
- AWS Migration Hub: Offers a centralized dashboard that provides complete visibility into the status and progress of application migrations across various AWS services. It helps streamline tracking, reduce complexity, and keep all stakeholders informed in real time.
- AWS Application Migration Service (MGN): Simplifies lift-and-shift migrations by automatically replicating physical, virtual, or cloud-based servers into AWS. It minimizes manual effort and downtime, allowing seamless transitions while maintaining source server settings, configurations, and network relationships.
- AWS Database Migration Service (DMS): Enables reliable database migrations with minimal downtime. It supports homogeneous and heterogeneous database replication, offers continuous data sync, and allows for real-time monitoring, making it ideal for moving mission-critical workloads to AWS.
- AWS Snowball and Snowmobile: Designed for secure, large-scale offline data transfers to AWS. They’re especially useful when internet connectivity is limited, providing encrypted physical devices that can transport terabytes or petabytes of data efficiently.
- AWS DataSync: Automates and accelerates secure data transfers between on-premises storage systems and AWS services like Amazon S3, EFS, or FSx. It supports scheduling, encryption, and detailed monitoring for efficient, enterprise-grade data movement.
As a team that specializes in AWS cloud migration services, we take care of the entire process — from assessment and planning to implementation and optimization. Our goal is to ensure a seamless transition, with minimal disruption to your operations and maximum long-term value.
Step 5: Prepare Your Cloud Environment
Before migrating any workloads, it’s essential to properly configure your AWS environment. This ensures a secure, scalable, and reliable foundation that aligns with your technical requirements, compliance needs, and long-term business objectives.
- Designing your target architecture: Use the AWS Well-Architected Framework to design a robust cloud environment. This ensures your architecture is scalable, secure, cost-optimized, and aligned with best practices across operational excellence, performance efficiency, reliability, security, and cost management.
- Setting up networking: Create a secure and efficient network infrastructure by configuring Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), IP address ranges, subnets, NAT gateways, and routing policies. These elements control traffic flow and ensure proper communication across your AWS resources.
- Implementing security and identity management: Leverage AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to define user roles and enforce least-privilege access. Set up multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and resource-level permissions to protect cloud assets and user credentials.
- Enabling monitoring and logging: Deploy monitoring tools like Amazon CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail, and AWS Config to track resource usage, system performance, and configuration changes. These services enable real-time insights, troubleshooting, and comprehensive audit logging for compliance and analysis.
- Ensuring compliance: Implement encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit. Configure backup strategies, enable data residency controls, and adhere to relevant compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2 to maintain regulatory readiness.
This phase lays the groundwork for a successful and secure AWS cloud migration, and mistakes here can lead to downtime, security risks, or compliance breaches.
Step 6: Migrate Applications and Data
With planning, tooling, and preparation complete, it’s time to begin the actual AWS cloud migration. Start by migrating to lower-risk workloads or test environments. Carefully monitor the process and document lessons learned for future phases.
Depending on your migration strategy, different AWS tools and approaches apply. Tailor your execution plan based on whether you’re rehosting, replatforming, or refactoring to ensure a smooth and efficient transition to the cloud.
- Rehosting: Use AWS Application Migration Service (MGN) to automate the lift-and-shift process. It replicates on-premises servers directly to AWS, minimizing downtime and manual effort while preserving your existing server configurations and operating system.
- Replatforming: Modify select application components during migration for improved performance or maintainability. For example, transition your database to Amazon RDS or migrate workloads to Amazon Linux for better compatibility, managed services, and long-term cloud optimization.
- Refactoring: Break down monolithic applications into microservices or migrate to modern architectures. Leverage services like Amazon ECS for containers, Amazon EKS for Kubernetes, or AWS Lambda for serverless computing to increase scalability, resilience, and development agility.
- For databases:
- Use AWS DMS – Break down monolithic applications into microservices or migrate to modern architectures. Leverage services like Amazon ECS for containers, Amazon EKS for Kubernetes, or AWS Lambda for serverless computing to increase scalability, resilience, and development agility.
- Perform data validation: After migration, verify data consistency between the source and target databases. Use validation tools to compare records, check integrity, and ensure your critical business data remains accurate and fully functional in the new environment.
Always validate the environment post-migration. Check application behavior, latency, data accuracy, performance, user access, and third-party integrations. Performance and reliability must meet or exceed pre-migration benchmarks.
Step 7: Optimize Post-Migration
Migration to AWS is just the beginning. After your systems are live, the next priority is continuous optimization—improving performance, managing costs, and embracing cloud-native capabilities to unlock the full value of your AWS investment.
- Monitor and Manage Performance: Use tools like Amazon CloudWatch Dashboards and AWS X-Ray to monitor system metrics, diagnose bottlenecks, and analyze end-to-end application performance. This ensures high availability and operational insight across all running services and resources.
- Right-Size Resources: Continuously evaluate instance performance and adjust resource sizes to match actual workload demands. This helps prevent over-provisioning, reduce unnecessary costs, and ensures your infrastructure remains efficient and cost-effective based on real-time usage.
- Implement Auto-Scaling: Configure EC2 Auto Scaling groups, AWS Lambda concurrency settings, or Elastic Load Balancing to automatically scale your application based on demand. This ensures consistent performance while optimizing resource usage and cloud spend during variable traffic.
- Enforce Cost Controls: Set financial thresholds and usage alerts with AWS Budgets. Use AWS Trusted Advisor and Cost Explorer to identify underutilized resources, optimize pricing models, and implement proactive cost-saving measures across all deployed AWS services.
After migration, consider refactoring legacy applications into serverless or containerized architectures. This allows you to fully leverage AWS-native services, improving scalability, resilience, and the ability to innovate faster with less operational overhead.
Step 8: Train Teams and Update Governance Policies
Successful AWS migration isn’t just about tools—it’s about people and processes. Equip your teams with the knowledge and governance structure needed to manage, optimize, and secure cloud environments effectively over time.
- Provide cloud training: Invest in employee development through AWS training programs, certification paths, and hands-on workshops. Focus on key roles like Cloud Architect, Security Engineer, and DevOps Specialist to build internal expertise and ensure operational efficiency in the cloud.
- Update governance policies: Revise governance to suit cloud operations. Establish clear policies around user access control, data privacy, regulatory compliance, cost tracking, and incident response to maintain security, transparency, and accountability across your AWS infrastructure.
- Review disaster recovery plans: Reevaluate existing disaster recovery strategies to ensure cloud readiness. Implement automated backups, real-time data replication, and rapid failover mechanisms to meet modern RTO/RPO requirements and guarantee business continuity in case of outages.
- Establish a Cloud Centre of Excellence (CCoE): Form a Cloud Center of Excellence—a dedicated team responsible for driving cloud adoption, setting best practices, guiding governance, and aligning AWS strategies with broader business goals across departments and organizational units.
For organizations with limited in-house expertise or those looking to accelerate their transformation, it’s often beneficial to partner with experienced cloud migration companies. These experts bring proven strategies, tools, and knowledge to support smooth transitions and ongoing optimization.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
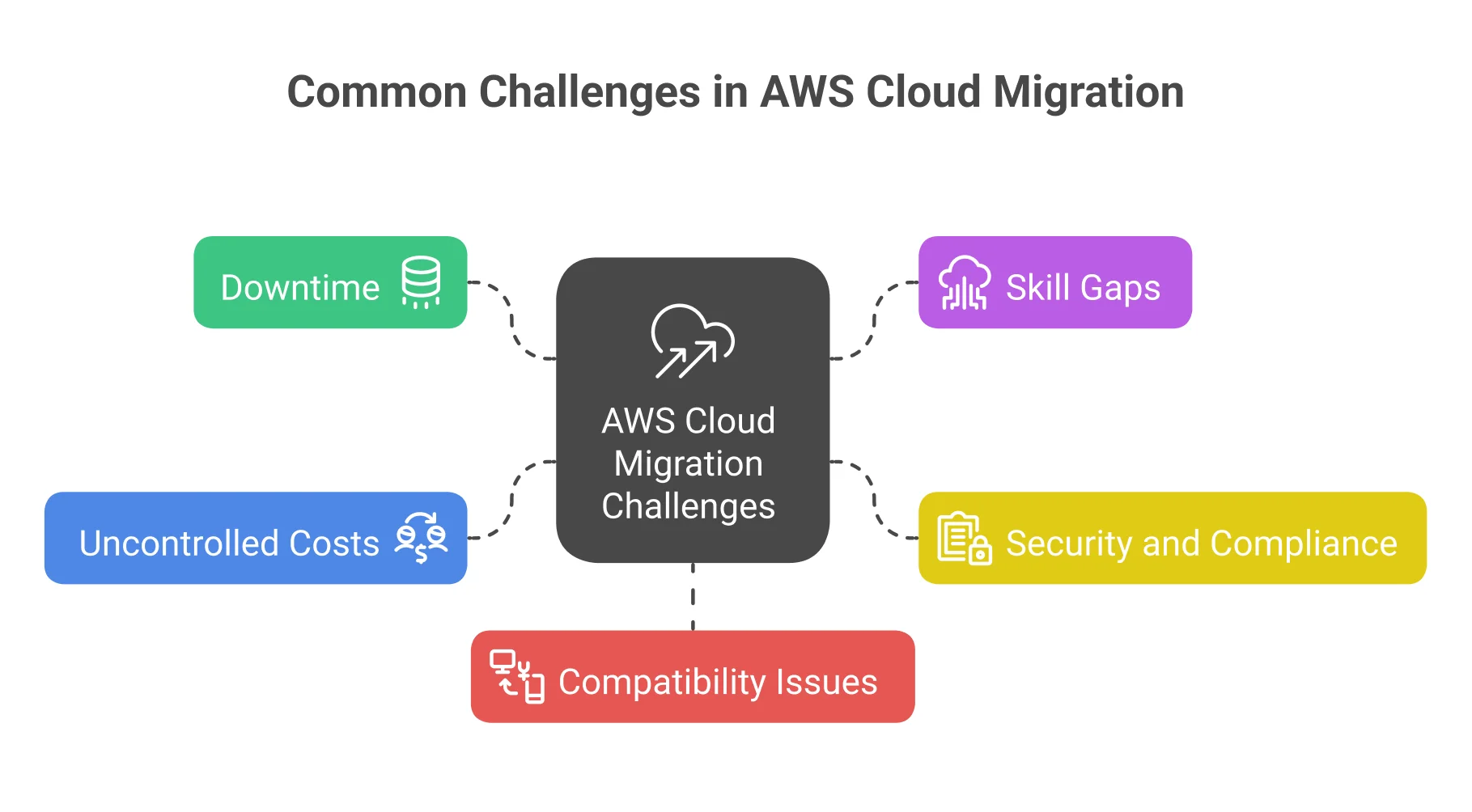
While AWS offers robust tools and frameworks, migrating to the cloud isn’t without its hurdles. Understanding common challenges and planning mitigation strategies early is essential for ensuring a smooth, secure, and cost-effective migration process.
- Downtime during migration: Unexpected downtime can disrupt operations and impact users. Mitigate this risk by using tools like AWS DMS and AWS MGN, which support continuous replication and cutover options to enable near-zero downtime during migration.
- Skill gaps: Lack of cloud expertise can slow progress or introduce risk. Address this by investing in upskilling your team through AWS training programs, or by partnering with certified AWS consultants to guide and accelerate the migration.
- Security and compliance: Security missteps can lead to vulnerabilities or non-compliance. Proactively configure AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), enable encryption for data in transit and at rest, and use tools like AWS Config for continuous compliance monitoring.
- Uncontrolled costs: Migrating without financial oversight may lead to unexpected expenses. Utilize AWS Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor to monitor resource usage, forecast future spending, and implement cost controls before inefficiencies accumulate across your cloud environment.
- Compatibility issues: Applications may rely on legacy systems or configurations that don’t translate directly to the cloud. Identify these dependencies early during your infrastructure assessment to plan updates, testing, or re-architecture where necessary before migration begins.
Anticipating potential challenges and proactively incorporating mitigation strategies into your AWS cloud migration plan is essential. This approach ensures minimal disruption, stronger security, cost control, and a smoother, more efficient transition to the cloud environment.
Final Thoughts
Migrating to AWS is a strategic move that offers immense benefits: enhanced scalability, global reach, robust security, and operational agility. However, these benefits can only be realized through meticulous planning, sound technical implementation, and ongoing optimization.
By following this step-by-step guide, organizations can navigate the complexities of AWS cloud migration with confidence. Whether you’re a startup seeking agility or an enterprise pursuing transformation, AWS provides the tools, support, and scalability to make cloud migration a true business enabler.
Above all, treat AWS cloud migration not just as a technical project, but as a cultural shift toward innovation, efficiency, and future-readiness.
Frequently Asked Questions
AWS Cloud Migration is the process of moving your digital assets—like servers, databases, applications, and data—from your on-premises setup or other cloud environments to Amazon Web Services (AWS). It’s about modernizing how your business operates, gaining flexibility, and cutting long-term IT costs.
There are plenty of good reasons—AWS offers scalable infrastructure, high availability, top-notch security, and cost-saving models like pay-as-you-go. Businesses move to AWS to boost performance, access cutting-edge technologies, and stay agile in a fast-changing market.
It can be—especially if you’re running large or legacy systems—but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With the right planning, tools, and team (or the help of AWS consultants), it becomes much more manageable. Starting small, like migrating one application first, is often the best way to learn and build confidence.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. A simple migration might take a few days or weeks, while a complex enterprise migration could take months. It depends on the size of your infrastructure, the type of applications, and your team’s readiness.
Not at all. Many companies go for a phased approach—moving low-risk workloads first, then scaling up as they learn. This reduces disruption and helps teams adjust to the new environment gradually.
Common hurdles include unexpected downtime, application compatibility issues, lack of in-house cloud expertise, or overspending due to poor cost planning. The good news? Most of these can be avoided with solid assessment and planning in advance.
Not necessarily. Some apps can be lifted and shifted “as is” using tools like AWS MGN. Others might need slight tweaks or full refactoring to perform optimally on the cloud. It depends on how your application is built and how much benefit you want from cloud-native features.
There’s a whole toolbox! AWS Migration Hub, AWS Application Migration Service (MGN), AWS Database Migration Service (DMS), and AWS DataSync are just a few. These tools help automate, monitor, and speed up your cloud migration.
Security is a top priority on AWS. You can use encryption, secure VPN connections, Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles, and strict access controls. It’s all about planning carefully and following AWS’s best practices for a secure setup.
Once you’re on AWS, the journey isn’t over—it’s just beginning! Post-migration tasks include performance tuning, cost optimization, monitoring, and possibly re-architecting your applications to better use cloud features. It’s also a good time to train your team and update your policies for cloud operations.
Yes! AWS offers programs like the Migration Acceleration Program (MAP), as well as certified partners who can guide you at every step. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, there’s support available.
In many cases, yes. You’ll move from fixed infrastructure costs to a more flexible pay-as-you-go model. But it’s important to monitor and manage usage to make the most of your investment—AWS provides tools like Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor for that.