Jul
How to Choose the Best Frontend Framework for Your Project

Introduction
Choosing the best frontend framework for your project can be the difference between a smooth development process and months of headaches. With dozens of frameworks available—each boasting unique features, communities, and strengths—it’s easy to get overwhelmed. Whether you’re building a simple blog or a large-scale enterprise application, making an informed decision is crucial. This comprehensive guide explores how to choose the best framework for frontend development, compares popular options, and dives into key factors like performance, scalability, and developer experience. Packed with statistics, expert opinions, and real-world use cases, this article helps you confidently decide on the best frontend frameworks for your needs.
Understanding Frontend Frameworks
When you’re building a website or web application, the frontend is what users actually see and interact with—buttons, forms, animations, navigation bars, and more. To create these elements efficiently and in a maintainable way, developers often use frontend frameworks. Think of a frontend framework as a ready-made toolbox filled with pre-written JavaScript code and best practices. It saves time, helps enforce structure, and ensures your project doesn’t become a tangled mess as it grows. These frameworks take care of some of the most complex parts of frontend development, like:
- Manipulating the DOM (Document Object Model): Instead of writing raw JavaScript to update every little element on the page, frameworks offer clean and optimized ways to do it. This means smoother, faster user interactions.
- Component-Based Architecture: Modern frameworks encourage building your UI out of reusable “components.” A button, a navigation bar, a login form—each of these can be designed as a standalone component and reused across your project. This makes code easier to manage, test, and scale.
- Routing: In single-page applications (SPAs), routing allows users to navigate between different views—like moving from a homepage to a profile page—without reloading the entire site. Frameworks provide built-in tools to manage these transitions seamlessly.
- State Management: State refers to the data that drives your app’s behavior—like whether a user is logged in or what items are in a shopping cart. Frontend frameworks help manage this state consistently across components and pages.
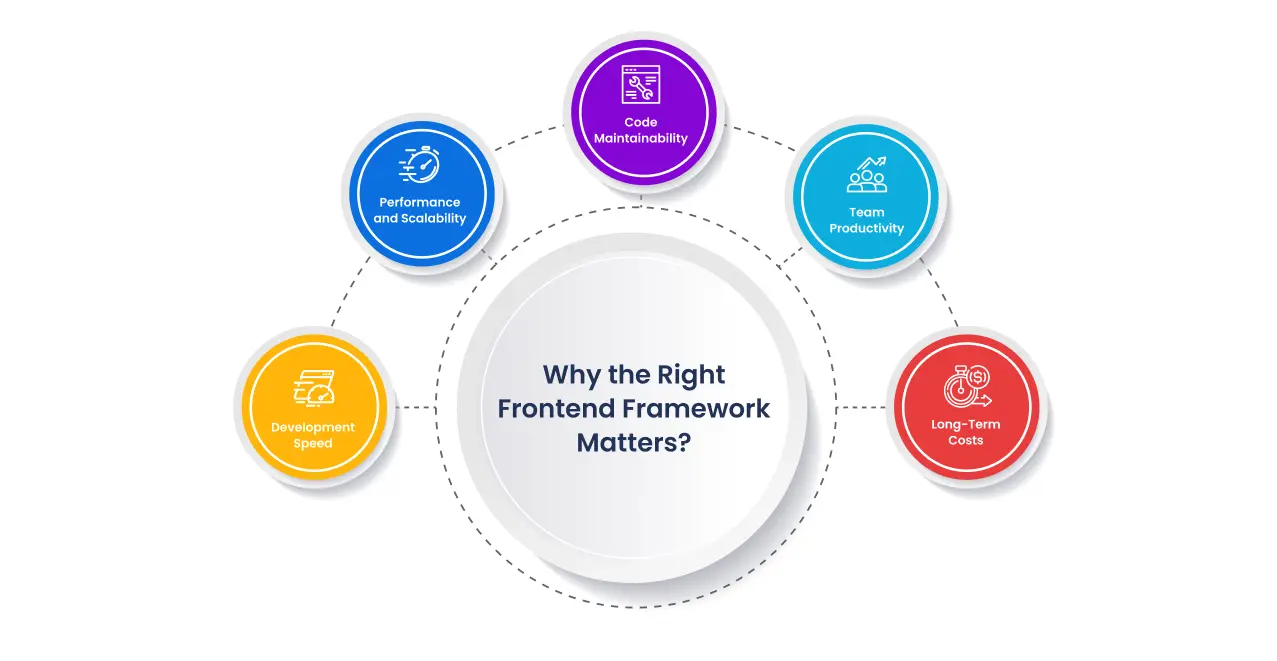
Why Choosing the Best Framework for Frontend Development Matters
When beginning a web project, one of the most important decisions your development team will face is selecting the best frontend framework. This decision goes far beyond personal preference; it can profoundly influence the overall success of your project. Choosing the best frontend framework directly affects the speed of development, ease of scalability, long-term maintainability, and ultimately determines how efficient and future-proof your web application will be in the long run.
1. Development Speed
A good frontend framework can accelerate development significantly. Most modern frameworks come with built-in features like component libraries, routing, and state management that save developers from having to reinvent the wheel. The more intuitive and well-documented the framework is, the faster your team can move. For startups and teams with tight deadlines, this can be the difference between launching on time and missing the market window. That’s why many businesses turn to experienced frontend professionals who understand how to make the most of these tools—ensuring clean code, seamless user experiences, and timely delivery.
2. Performance and Scalability
Not all frameworks are built to handle the same scale. If your project is expected to grow—whether in terms of user base, features, or data—your frontend stack needs to scale with it. Frameworks like React (used by Facebook) and Next.js (used by Hulu and Twitch) have proven they can handle high-traffic, performance-intensive environments. Choosing a lightweight or poorly optimized framework might work for small apps but could lead to major slowdowns as your app grows.
3. Code Maintainability
As your codebase expands, managing and maintaining it becomes increasingly complex. A well-structured framework helps organize your code, reduce duplication, and make it easier for multiple developers to collaborate. Frameworks that enforce strict patterns and modular components—like Angular and Vue.js—help ensure your app remains maintainable even after years of updates. This becomes crucial when onboarding new developers or revisiting legacy code.
4. Team Productivity
Different frameworks have different learning curves. A framework that aligns with your team’s existing skill set will make onboarding smoother and daily development more productive. For example, teams familiar with TypeScript often lean toward Angular or Next.js because of their built-in TypeScript support. On the other hand, Vue.js is known for being beginner-friendly, making it easier for newer developers to contribute quickly.
5. Long-Term Costs
The wrong choice can become expensive—fast. If your app hits a wall with performance or your framework lacks the flexibility to support future features, you may be forced into a costly rewrite. Similarly, frameworks with smaller communities may lack third-party plugins or developer support, leading to more custom development and increased overhead. Choosing a framework that’s well-supported, widely adopted, and continuously updated helps future-proof your project.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Best Frontend Framework
When choosing the best frontend framework for your project, it’s important to make a well-informed decision that aligns with your goals, development approach, and future growth plans. The right choice can streamline development and improve user experience.
1. Project Requirements
- Is it a single-page application (SPA) or multi-page?
- Will it handle real-time updates, animations, or complex UI interactions?
Determine whether the application requires seamless user navigation within a single page or multiple pages for different functionalities, which affects routing, loading speed, and user experience.
Evaluate if the application needs dynamic content updates, smooth animations, or advanced user interface behavior, as these will impact the choice of frameworks, performance strategy, and development complexity.
2. Learning Curve and Team Skillset
Choose a framework that matches your team’s current skill level. A highly powerful tool like Angular may be overkill for small teams, while React or Vue.js offer flexibility and ease.
- Stat Insight: React, for instance, boasts over 220,000 stars on GitHub, reflecting its extensive community support, vast ecosystem, and reputation for being beginner-friendly while still powerful enough for enterprise-grade applications.
3. Performance and Speed
Some JavaScript frameworks are specifically optimized to deliver superior rendering speed and overall application performance. This becomes crucial when building interfaces that require frequent updates or complex user interactions.
- React, for example, leverages a virtual DOM—an in-memory representation of the real DOM—which allows it to efficiently calculate the minimal number of changes needed and apply them in batches. This results in faster and smoother updates to the user interface, enhancing performance without overburdening the browser.
- Svelte, on the other hand, takes a different and innovative approach. It compiles your application’s components into highly efficient JavaScript code at build time, rather than relying on a virtual DOM at runtime. This significantly reduces the runtime overhead and leads to snappier, more responsive applications with minimal resource consumption.
4. Community and Ecosystem
A framework’s community size and ecosystem play a critical role in long-term development success. The larger and more active the community, the easier it becomes to access helpful resources, whether it’s through extensive documentation, third-party plugins, tutorials, or forums. Developers benefit from shared knowledge, open-source contributions, and quicker resolutions to bugs or technical challenges.
- For example, React is backed by one of the largest communities in the front-end ecosystem. Its modular nature allows seamless integration with a wide range of libraries. Key tools include Redux for predictable state management, React Router for efficient navigation, and Next.js for server-side rendering, routing, and performance enhancement. Together, these tools form a rich ecosystem that makes building scalable, high-performing applications easier and more efficient.
5. Mobile and Desktop Support
If your application is intended to run seamlessly across multiple platforms—such as web, mobile, and desktop—it’s essential to choose a framework that offers robust cross-platform development capabilities. This ensures code reusability, consistent user experience, and reduced development time and maintenance efforts.
- React Native, built on top of React, is a popular choice for developing high-performance mobile applications for both iOS and Android using a shared codebase. It provides a native look and feels while leveraging the flexibility of JavaScript and React’s component-driven architecture.
- For desktop application development, Electron is a powerful framework that enables the creation of cross-platform desktop apps using standard web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It wraps web applications into desktop environments and is widely used for apps like Visual Studio Code and Slack, offering native-like performance and access to system resources.
6. Scalability and Maintainability
- When building applications intended to grow in size or complexity over time, scalability and maintainability become top priorities. A well-structured framework should support component-based architecture, allowing developers to break down the UI into reusable, manageable pieces. Features like code-splitting and integration with modern module bundlers (e.g. Webpack, Vite) help optimize performance and organization as the application evolves.
- Angular, known for its strict conventions and fully integrated tooling, is especially suited for large-scale enterprise-level projects. Its opinionated structure enforces best practices, improves code consistency across teams, and enhances long-term maintainability—making it ideal for applications with extensive business logic, modular workflows, and long-term support requirements.
7. SEO Capabilities
If your application is content-driven, marketing-focused, or relies heavily on organic search traffic, then search engine optimization (SEO) should be a core consideration during framework selection. Traditional single-page applications often face challenges with SEO, as content is rendered client-side, which can limit search engine visibility.
- To address this, frameworks that support server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation (SSG) are highly beneficial. Next.js, a powerful React-based framework, excels in this area by offering built-in SSR, enabling pages to be rendered on the server before being sent to the browser. This approach enhances crawlability, improves load times, and increases visibility on search engines—making it a top choice for SEO-friendly web applications.
8. Corporate Backing
When choosing a development framework, corporate backing can be a strong indicator of its stability, continuous improvement, and long-term viability. Frameworks supported by major tech companies typically benefit from regular updates, performance optimizations, security patches, and a clear development roadmap—all of which are crucial for enterprise-level or mission-critical projects.
- React, for instance, is maintained by Meta (formerly Facebook) and is widely used in many of their core products, ensuring it receives consistent investment and innovation. Angular, on the other hand, is developed and supported by Google, giving it a strong foundation, particularly for enterprise-scale applications with strict architectural requirements.
- While Vue.js began as an independent open-source project created by Evan You, it has since gained strong traction and support within large ecosystems like Alibaba and Laravel. This community-driven yet commercially supported model has helped Vue mature into a reliable, well-documented, and widely adopted framework.
Quick Comparison of the Best Frontend Frameworks
Here’s a quick comparison of some of the best frontend frameworks available today, highlighting their key strengths, use cases, and performance benefits to help you choose the right one based on your project’s needs and development goals.

1. React
Modern frontend development offers a wide variety of JavaScript frameworks, each with its own strengths, complexity, and ideal use cases. React, developed by Meta (Facebook), is one of the most popular libraries in the developer world. It has a medium learning curve, owing to concepts like JSX and state management, but delivers high performance. With a massive global community, React is highly supported and frequently updated. It is best suited for building versatile applications and Single Page Applications (SPAs), making it a staple in both startups and large enterprises.
2. Angular
Angular, maintained by Google, is a full-fledged MVC (Model-View-Controller) framework known for its structured and robust architecture. It comes with a steep learning curve, primarily because of its extensive feature set and reliance on TypeScript. However, Angular also offers high performance, thanks to features like Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation and RxJS. It has a large developer community and is widely adopted by enterprises for developing complex, large-scale applications that require strict organisation and scalability.
3. Vue.js
Vue.js, created by Evan You, takes a middle ground by offering the power of a modern framework with the simplicity of basic JavaScript. It is easy to learn, with a gentle learning curve that appeals to beginners and solo developers. Despite its simplicity, Vue delivers high performance through its reactive system and component-based architecture. Its growing community ensures steady support and evolution. Vue is ideal for progressive web apps and is often the framework of choice for small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) looking for quick and efficient development.
4. Svelte
Svelte, developed by Rich Harris, introduces a radically different approach to frontend development. Unlike traditional frameworks, Svelte compiles components to highly optimised vanilla JavaScript at build time, removing the need for a virtual DOM. This results in very high performance and leaner, faster apps. Svelte is easy to learn and eliminates much of the boilerplate code, which accelerates development. Its emerging community is steadily growing as more developers are drawn to its simplicity and efficiency. Svelte is best suited for high-performance applications where speed and responsiveness are critical, such as interactive interfaces and lightweight tools.
5. Next.js
Next.js, created by Vercel, builds upon React by adding key capabilities like Server-Side Rendering (SSR), Static Site Generation (SSG), and API routes. These features enable high performance, especially for applications where SEO, fast load times, and dynamic content are important. It has a medium learning curve, requiring familiarity with both React and Next.js-specific features like routing and data fetching strategies. The rapidly growing community around Next.js makes it a preferred choice for SEO-friendly applications, including blogs, marketing sites, and large-scale content-driven platforms like eCommerce stores.
Case Studies of Companies Using Best Frontend Frameworks
One of the best ways to understand the power and reliability of the best frontend framework is by examining which companies use it in real-world applications. These aren’t limited to small businesses—many of the world’s leading brands rely on the best frontend framework to build fast, scalable, and interactive digital platforms. These examples highlight how choosing the best frontend framework can drive performance and user engagement across large-scale projects.
1. Facebook: Powered by React
React was originally created by Facebook (now Meta), so it’s no surprise that the social media giant uses it extensively. From the news feed to chat features and notifications, React helps manage complex user interactions at scale. One of React’s biggest strengths is its virtual DOM, which ensures updates to the UI happen quickly and efficiently critical for an app that serves billions of users daily. React also allows Facebook to reuse components across its ecosystem, including on Instagram and WhatsApp Web.
2. Google Ads: Built on Angular
Angular, developed and maintained by Google, is the backbone of some of the company’s most data-intensive platforms—most notably, Google Ads. Angular’s strong support for enterprise-level development, two-way data binding, and dependency injection makes it ideal for applications like Google Ads, where real-time data and form handling are crucial. It’s also fully TypeScript-based, giving developers better tooling and maintainability over time.
3. Alibaba & Xiaomi: Vue.js in Action
Vue.js may have started as a grassroots framework, but it quickly caught the attention of large corporations—especially in Asia. Alibaba and Xiaomi, two of China’s biggest e-commerce and tech players, use Vue.js to power parts of their front-end architecture. Vue’s approachable learning curve and flexibility make it perfect for teams that want a robust but lightweight solution. It also fits well into existing projects, allowing for gradual adoption.
4. Square Enix: Game-Changing with Svelte
Square Enix, the gaming company behind titles like Final Fantasy and Tomb Raider, has experimented with Svelte for some of its web-based projects and internal tools. What makes Svelte different is that it compiles your code to pure JavaScript at build time, meaning there’s no heavy framework running in the browser. This results in lightning-fast performance—a big win for user experiences in the gaming industry where even milliseconds count.
5. Hulu & Twitch: Going Seamless with Next.js
Next.js, built on top of React, is designed for performance and scalability. Hulu and Twitch, both streaming platforms with millions of users, leverage Next.js for its server-side rendering and static site generation capabilities. These features make content load faster, improve SEO, and deliver smoother performance across devices. For services that serve rich media and live content, speed and efficiency are everything—and that’s exactly where Next.js shines.
These examples show how best frontend frameworks aren’t just academic tools—they’re battle-tested by companies with huge performance and usability demands. Whether it’s managing social interactions, delivering ads, running e-commerce sites, or streaming live content, each framework has carved out a niche where it excels.
Trends and the Future of Best Frontend Frameworks
Frontend development is progressing rapidly, and what once delivered results may now fall short of modern expectations. Today’s users demand faster performance, greater scalability, and a smoother user journey. As the digital landscape shifts, adopting the best frontend framework becomes essential. With innovative tools and frameworks emerging every year, staying current requires a clear understanding of where the industry is going and how the best frontend framework can support future growth.
1. The Rise of Compile-Time Optimized Frameworks
Traditionally, the best frontend framework was judged by its runtime performance—how quickly it could update the DOM, manage application state, and respond to user actions in the browser. Today, there’s a growing shift towards compile-time optimization. This evolution means that the best frontend framework now performs much of the heavy lifting before your code ever reaches the browser, delivering faster load times and improved performance without relying heavily on runtime overhead.
Two strong contenders in this new era of compile-time focus are Svelte and SolidJS—both gaining traction as the best frontend framework options. As reported by the State of JS 2023 survey, developer interest in these tools is rising fast. Svelte compiles components into highly efficient JavaScript without any runtime, reducing bundle size significantly. SolidJS, on the other hand, delivers fine-grained reactivity and impressive speed, proving itself a serious rival to traditional libraries.
2. AI Meets Frontend Development
Another trend shaking up the front-end world is the integration of AI-powered tools directly into the development process. These aren’t just chatbots or assistants—they’re actual coding partners. Tools are emerging that can auto-generate UI components, suggest layout structures, or even write boilerplate code based on your project’s needs. And frameworks are beginning to adapt to these tools by offering better APIs, plugin systems, and integrations that streamline this process.
This doesn’t mean developers are being replaced—but it does mean their workflows are getting much more efficient. Imagine dragging and dropping a UI design and having the code auto generated in your chosen framework, with responsiveness and accessibility already considered. That’s no longer a futuristic concept—it’s happening now.
3. Edge-Ready and Performance-First Architectures
As users increasingly expect lightning-fast apps no matter their location, the best frontend framework must adapt to new performance challenges. This has led to a reimagining of how web applications are rendered and delivered. Enter Qwik and Astro—two innovative contenders for the best frontend framework title. Both prioritize speed and efficiency by focusing on partial hydration and server-side rendering, ensuring minimal JavaScript is sent to the browser and maximizing load performance globally.
- Qwik introduces a revolutionary take on the best frontend framework by only loading JavaScript when it’s absolutely required. Its standout feature—“resumability”—means the app is server-rendered and instantly interactive in the browser, skipping the usual rehydration step. This leads to ultra-fast page loads and an exceptional user experience. By eliminating unnecessary scripts, Qwik is setting a new performance standard, proving itself as a serious contender for the title of best frontend framework.
- Astro embraces the “islands architecture” model, making it a strong candidate for the best frontend framework. It renders most of the content on the server and only hydrates interactive components, drastically reducing the JavaScript sent to the browser. This method ensures faster load times and excellent performance. Supporting multiple frameworks like React, Vue, and Svelte within a single project, Astro offers developers unmatched flexibility without compromising speed or scalability.
These frameworks are designed with edge computing in mind, allowing them to serve content from servers nearest to the user. This approach makes the best frontend framework even more powerful by reducing latency, improving load times, and delivering faster, more responsive digital experiences across the globe.
4. Looking Ahead
As Alan Kay once said, “The best way to predict the future is to invent it.” That’s exactly what today’s frontend community is doing—driving innovation through smarter tools, smaller bundles, and advanced automation techniques. By constantly rethinking how we build and deliver web applications, developers are shaping the future of the web. At the centre of this progress is the quest to define the best frontend framework for speed, scalability, and user experience.
In the coming years, we can expect:
- Greater use of AI in the development workflow: AI will increasingly assist developers by automating repetitive coding tasks, suggesting optimizations, and enhancing testing—making it easier to adopt the best frontend framework for smarter, faster builds.
- Even leaner frameworks focused on speed: The next generation of the best frontend framework will emphasize smaller bundles, minimal JavaScript, and lightning-fast performance, ensuring faster load times and improved user experiences across all devices and networks.
- Serverless-first architectures: Future applications using the best frontend framework will likely adopt serverless-first strategies, offering better scalability, reduced backend maintenance, and seamless integration with edge computing for instant global access and performance.
- Better developer experience without sacrificing performance: The best frontend framework will continue to evolve, offering streamlined tooling, real-time collaboration, and improved debugging—empowering developers to build faster, without compromising on code quality or runtime performance.
Choosing the Best Frontend Framework in 2025
Let’s face it—choosing the best frontend framework can feel overwhelming. With so many options out there, it’s easy to fall into the trap of picking the most popular one without considering your project’s unique needs. The truth is there’s no universal “best frontend framework”—only the best one for your specific use case. Think of it like choosing a vehicle. A sports car might be fast and flashy, but it’s not ideal for hauling furniture. Likewise, your project type should dictate which framework you go with.
Here’s a breakdown to help guide your decision in 2025:
1. For Small Projects or MVPs
If you’re building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) or a lightweight app, your priority is probably speed, simplicity, and flexibility. In this case, you want something that gets you to the market fast without a lot of overhead.
- Vue.js is great here—it’s easy to learn, has strong community support, and lets you scale up gradually as your app grows.
- Svelte is also a top contender. Since it compiles down to vanilla JavaScript, there’s no runtime burden, and your app stays lightning-fast even with minimal optimization. Plus, the syntax is clean and beginner friendly.
2. For Large-Scale Applications
When you’re dealing with enterprise apps, dashboards, or complex ecosystems, structure and scalability are key.
- Angular shines here. It offers a complete, opinionated solution with built-in routing, dependency injection, and strong TypeScript support. Big teams often benefit from its consistency and tooling.
- React, though more flexible and less opinionated, is another strong choice—especially if your team prefers building their own architecture with community-driven tools. React’s massive ecosystem means you’ll never run out of third-party solutions.
3. For SEO-Focused Applications
If SEO is at the heart of your app—say, you’re building a blog, e-commerce site, or marketing page—you need a framework that handles server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation (SSG).
- Next.js is a top pick here. Built on React, it combines SSR, static generation, and API routes, giving you great flexibility while still delivering SEO-friendly content fast.
- Astro is a newer player, but it made a huge splash with its “islands architecture,” which only sends JavaScript for interactive parts of the page. For content-heavy sites with minimal interactivity, Astro is blazing fast.
4. For Cross-Platform Development
Sometimes, you want to write code once and deploy it everywhere—web, iOS, Android.
- React Native is the go-to for mobile apps built with JavaScript. It shares logic with React, which means your team can build for mobile using familiar syntax.
- Flutter, while not strictly a frontend framework (it’s Dart-based), deserves mention. It’s incredibly performant and offers beautiful native-like UIs across all platforms. Great if you’re starting from scratch and want tight control over design and animations.
Ask These Questions Before You Choose:
Before you commit to any framework, pause and consider these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- Do you need real-time features?
- How quickly does it need to scale?
If you’re aiming for users in low-bandwidth areas, choose lightweight frameworks like Svelte or Astro.
For chat apps, live dashboards, or anything dynamic, React (with tools like Socket.io or Firebase) or Angular (with RxJS) can serve you well.
If you expect your app to grow fast and support lots of contributors, Angular’s structure or React’s modularity will help keep things maintainable.
Final Thoughts
The best frontend framework is the one that aligns with your project’s goals, team expertise, and future roadmap. React might suit some teams, while others thrive with Vue.js or Svelte.
Remember, frameworks are tools. Like any craftsman, your success depends more on how you use the tool than which one you choose.
Quote: “Tools amplify our capabilities. It’s not about replacing skills, it’s about extending them.” —Brett Victor
Frequently Asked Questions
Vue.js or Svelte are often considered beginner-friendly best frontend frameworks due to their simple syntax and ease of integration.
Next.js stands out as the best frontend framework for SEO due to its powerful server-side rendering capabilities and comprehensive built-in search engine optimization features.
React remains highly popular due to its large community, reusable components, and ecosystem, but other options like Svelte and Vue are catching up.
Svelte is considered the most lightweight frontend framework because it compiles code at build time, resulting in faster load times and highly optimized, minimal JavaScript output.
While it’s technically possible to combine multiple frontend frameworks, doing so often leads to complex code conflicts, larger bundles, and significantly more difficult maintenance over time.
When it comes to building large-scale applications, Angular and React are widely considered the best frontend frameworks.
When it comes to community support, React stands out as the best frontend framework, with an enormous ecosystem of developers, resources, libraries, and forums.
Yes, especially if performance and modern architecture are your priorities, but they may lack the maturity and ecosystem of older frameworks.
Absolutely. Having a strong foundational understanding of JavaScript is crucial, as all frontend frameworks are built on top of core JavaScript concepts and functionality.
A frontend framework provides a complete structure for building applications, including routing, state management, and component rendering. A library like React focuses on one aspect (UI) and lets you choose the rest of the architecture.