Jul
Step-by-Step Guide to Web Development

In today’s digital-first landscape, a strong online presence is vital for businesses of all sizes. A well-crafted website is more than just a digital brochure—it’s a powerful tool for engaging users, driving conversions, and delivering real value. Whether you need a basic informational site or a complex web application, this guide to web development will help you understand each stage of the process and make informed decisions throughout.
Whether you’re a business owner looking to launch a new site or a developer just getting started, these beginners guide to web development covers everything from planning and design to deployment and maintenance.
What is Web Development?
Web development is the process of building websites and web applications for the internet. It ranges from simple static sites to complex platforms like e-commerce stores and social networks. A complete web solution typically involves three key components: the front-end, back-end, and database management. Each plays a crucial role in delivering responsive, secure, and functional websites tailored to both user needs and business objectives.
- Front-end (Client-side)
- Back-end (Server-side)
- Database Management
This is the visual layer users interact with. It includes HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, often using frameworks like React or Vue.js to create dynamic, responsive, and visually engaging interfaces.
The back-end handles server logic, processes data, and manages user authentication. Technologies include Node.js, Python, PHP, or Java, enabling smooth interaction between the user interface and databases.
Databases store, organize, and retrieve application data efficiently. Common systems include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB—ensuring reliability, fast access, and secure storage of user and business data.
Why Web Development Matters
A professionally developed website is more than a digital requirement—it’s a powerful tool for business growth. It enhances brand credibility, improves user experience, and increases visibility in search engines. Effective web development supports marketing goals, boosts customer engagement, and drives conversions. By investing in quality web development, businesses can build trust, streamline operations, and create lasting impressions that turn visitors into loyal customers.
1. Establish a Digital Presence
Your website is often the first impression potential customers get. A professionally built site enhances credibility, improves trust, and ensures your business is accessible around the clock, worldwide.
2. Improve User Engagement
Modern websites prioritize interactive design and user experience. Effective UI/UX encourages visitors to explore further, increasing dwell time and significantly boosting your chances of leads, conversions, or repeat visits.
3. Streamline Business Operations
Websites can automate tasks like user registration, bookings, payments, and customer support. These integrated features reduce manual workload and enhance operational efficiency, allowing you to focus on growth.
4. Ensure Scalability
A well-structured website is built to grow with your business. It allows seamless integration of new features and technologies, supporting future needs without requiring major redevelopment or redesign.
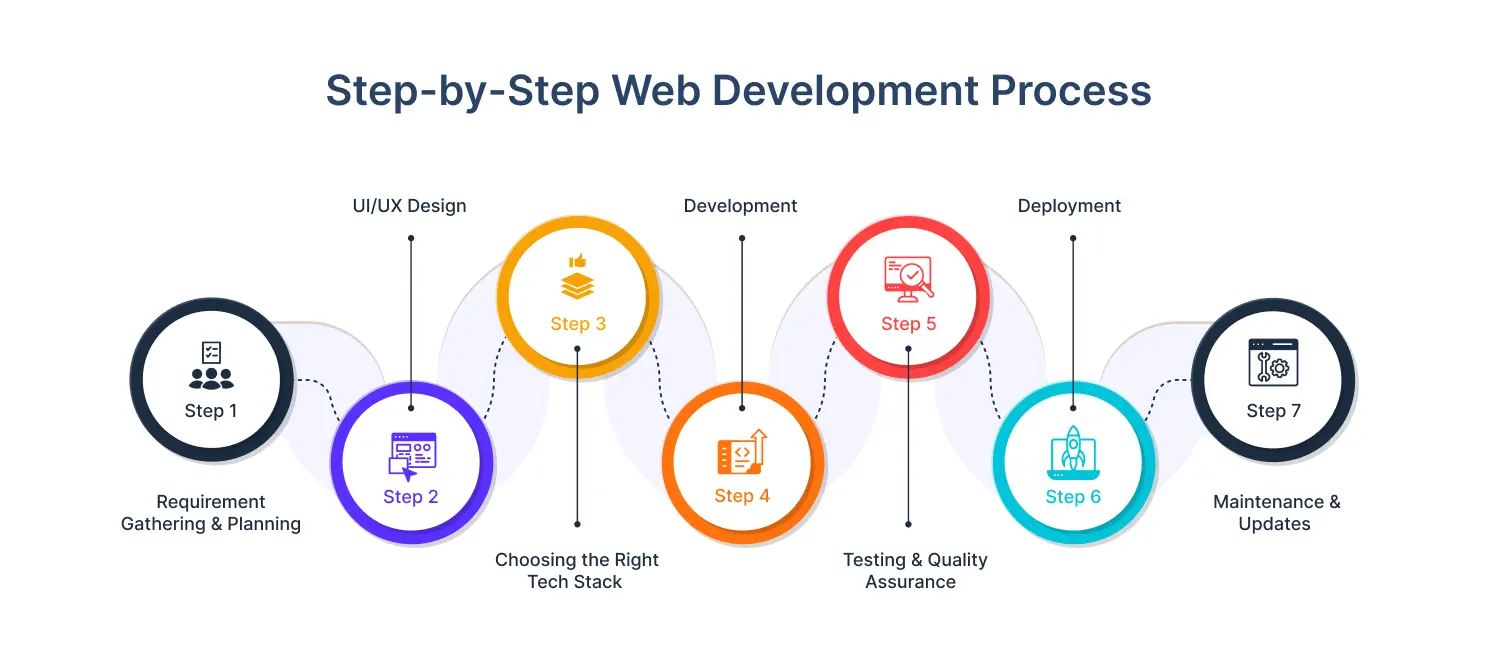
Step-by-Step Web Development Process
Step 1: Requirement Gathering & Planning
Begin by clearly outlining what you want your website to accomplish. Whether it’s an eCommerce platform, a blog, or a corporate site, effective planning ensures everything aligns with your goals. This stage forms the foundation for design, development, and launch. Taking the time to structure your ideas, define requirements, and consider the user journey will help avoid costly changes later in the process.
Tasks:
- Identify target audience and business goals
- Define site architecture and required features
- Set timelines and budgets
- Create a Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
Understand who your users are and what your website should achieve—be it lead generation, sales, or information sharing. Clear goals guide the structure and overall user experience.
List key pages, core functions, and how users will navigate. Defining these elements early helps developers and designers work more efficiently and ensures nothing critical is overlooked.
Establish realistic deadlines and financial limits. This ensures the project stays on track and avoids unexpected delays or expenses during development or post-launch refinement stages.
Document every technical and functional requirement clearly. An SRS ensures all stakeholders and developers are aligned and reduces the chances of miscommunication throughout the development cycle.
Pro Tip: Use mind-mapping tools or flowcharts to visualize how users will move through your site. It simplifies decision-making, clarifies objectives, and helps refine your content and navigation structure.
Step 2: UI/UX Design
Design goes beyond how a website looks—it influences how users interact with it. A thoughtful, user-focused design improves satisfaction, retention, and conversions. Intuitive navigation, a clean layout, and responsiveness are essential. The goal is to ensure the design aligns with user expectations while reflecting your brand identity. Investing time in UI/UX at this stage helps avoid usability issues later and ensures your site delivers a smooth, consistent experience across all devices.
Tasks:
- Create wireframes and mockups
- Define color schemes, typography, and branding elements
- Design mobile-friendly layouts
- Build prototypes using Figma or Adobe XD
Sketch rough layouts and screen structures before full design begins. Wireframes help visualize content placement, allowing early feedback and refinements before moving on to detailed mockups.
Choose a cohesive color palette, font pairings, and brand visuals that reflect your identity. These elements create consistency and reinforce recognition across the site and other digital touchpoints.
Prioritize mobile usability by designing layouts that adapt to smaller screens. Mobile-first thinking ensures accessibility and improves performance for the majority of users who browse on handheld devices.
Prototypes simulate user interaction before coding begins. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD help test user flow, gather feedback, and fine-tune details without heavy development costs.
Pro Tip: Always prioritize usability. Make navigation straightforward, consistent, and accessible to all users—including those with impairments—to deliver a genuinely inclusive and user-friendly experience.
Step 3: Choosing the Right Tech Stack
Your technology stack determines how well your website performs, scales, and handles security. It’s the foundation of your build, combining front-end, back-end, database, and hosting technologies. Selecting the right stack means balancing technical requirements with the skills of your development team. A suitable stack ensures long-term stability, easier maintenance, and the flexibility to grow your platform as business needs evolve.
Tasks:
- Front-end: HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, React, Angular, or Vue.js
- Back-end: Node.js, Django, Ruby on Rails, PHP
- Database: MongoDB, PostgreSQL, MySQL
- Servers: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure
The front-end controls everything users see and interact with. Using modern technologies ensures a responsive, fast, and visually engaging interface compatible across browsers and screen sizes.
The back-end handles logic, server communication, and data processing. Choose tools that best support your app’s complexity, integration needs, and the capabilities of your development team.
Databases store and retrieve your site’s data. The right choice depends on your data structure, speed needs, and how relationships between information are managed within the application.
Reliable cloud hosting platforms ensure performance, uptime, and data security. Each offers scalability, global access, and tools to support modern web applications of varying sizes and traffic.
Pro Tip: Always match your tech stack to your project’s technical needs and the expertise available. A well-matched stack reduces future roadblocks and improves your app’s development and maintenance experience.
Step 4: Development
With your design finalized and tech stack selected, development begins. This phase is typically organized into stages or sprints to ensure steady progress and manageable testing. Developers work on both front-end and back-end components, integrating services and databases along the way. Communication between teams is crucial at this stage to maintain consistency, prevent bottlenecks, and ensure the build aligns with the original project scope and user expectations.
Tasks:
- Code the front-end interface
- Build back-end functionality (authentication, APIs, data handling)
- Integrate third-party services like payment gateways or analytics
- Set up database schemas
Front-end developers translate designs into responsive, interactive code using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks—ensuring the site looks and functions as intended across all screen sizes and browsers
Back-end development involves creating user login systems, APIs, and data processing logic. These features ensure secure user access, efficient communication between systems, and reliable content delivery.
Third-party tools such as Stripe, PayPal, or Google Analytics are integrated to support key functions like payments, tracking, or communication—enhancing the app’s overall capability and user experience.
Properly structured database schemas define how data is organized, stored, and retrieved. A logical schema improves performance, avoids redundancy, and supports reliable application behavior across all features.
Pro Tip: Use Git for version control and implement peer code reviews. This encourages clean, consistent coding practices, simplifies collaboration, and helps track and roll back changes if needed.
Step 5: Testing & Quality Assurance
Testing is a critical step that ensures your website performs reliably across different devices, browsers, and user
scenarios. It helps identify bugs, usability issues, and performance bottlenecks before launch. A thorough quality assurance process safeguards user experience and builds trust. Multiple testing methods should be used to verify functionality, security, and compatibility—ultimately ensuring that your final product is stable, secure, and ready for public release.
Types of Testing:
- Functional Testing: Ensures core features work
- Usability Testing: Evaluates user experience
- Performance Testing: Checks speed and responsiveness
- Security Testing: Identifies vulnerabilities
This verifies that all key functions—such as forms, navigation, and user logins—perform correctly and consistently, as expected, throughout the site on both desktop and mobile platforms.
Real users or testers interact with the site to assess navigation ease, clarity of layout, and design intuitiveness, ensuring the interface is accessible, consistent, and user-friendly.
This tests how quickly your site loads and responds to user actions under different conditions, helping identify and resolve lag, crashes, or delays during peak usage.
Security testing checks for potential threats like SQL injection, data leaks, or weak authentication. It ensures the site meets best practices for protecting user data and preventing breaches.
Pro Tip: Automate regression testing using tools like Selenium or Jest to detect bugs quickly when new updates are made—saving time and maintaining quality across versions.
Step 6: Deployment
Once testing is complete and your site meets all requirements, it’s time to launch. This phase involves configuring servers, domains, and security certificates before going live. Proper deployment ensures your site is stable, secure, and fully functional for public access. It’s important to carry out a final review before release, ensuring that everything runs smoothly and that your users have a seamless experience from day one.
Tasks:
- Final server setup
- Configure hosting and domain
- Set up SSL and HTTPS
- Launch the site
Prepare your production environment by configuring web servers, firewalls, and necessary services. Ensuring everything is correctly aligned helps prevent downtime and supports a smooth transition from staging.
Connect your chosen domain to a reliable hosting provider. This step ensures your site is accessible worldwide and hosted on a platform that matches your scalability and performance needs.
Secure your website by installing an SSL certificate and enforcing HTTPS. This protects user data, builds trust, and improves search rankings by ensuring a secure, encrypted connection.
Once all systems are tested and confirmed, go live. Monitor closely for any issues, and be prepared to resolve them quickly to maintain a flawless user experience post-launch.
Pro Tip: Implement CI/CD pipelines to automate deployments. This streamlines code releases, reduces manual errors, and ensures faster, more reliable updates across development, staging, and production environments.
Step 7: Maintenance & Updates
Launching your website is just the beginning. Ongoing maintenance is essential to keep your site secure, functional, and relevant. Regular updates, monitoring, and optimization ensure users enjoy a smooth experience while your platform stays competitive. Maintenance also allows you to respond to user feedback, address technical issues, and adapt to evolving business needs—making your website a continuously improving asset rather than a one-time project.
Tasks:
- Monitor server uptime and performance
- Patch bugs and vulnerabilities
- Add features based on user feedback
- Update content regularly
Keep track of how your site performs in real time. Monitoring helps detect slowdowns or outages quickly, so you can resolve issues before they impact users or your reputation.
Fixing bugs and closing security loopholes keeps your site safe. Prompt attention to updates helps prevent data breaches, enhances stability, and ensures compliance with security standards.
User feedback offers valuable insight into improvements. Adding requested features enhances satisfaction, builds loyalty, and ensures your site evolves in line with real user expectations.
Fresh content keeps your site relevant and improves search rankings. Regularly updating blogs, product pages, or news sections shows that your business is active and engaged.
Pro Tip: Schedule backups and audits routinely. This protects your data, ensures restore options in emergencies, and allows you to catch errors or outdated elements before they become real problems.
Key Features to Consider in Web Development
1. Responsive Design
Design your website to automatically adjust for different screen sizes—mobile, tablet, or desktop—so users enjoy a consistent, intuitive experience regardless of the device they’re browsing from.
2. SEO-Friendly Structure
Use descriptive URLs, proper meta tags, structured sitemaps, and alt text for images. These elements improve search engine visibility and help your site rank higher in relevant search results.
3. Fast Load Time
Improve page speed by compressing images, reducing file sizes, minifying CSS/JavaScript, and enabling browser caching. A fast-loading site keeps users engaged and boosts overall SEO performance.
4. Secure Architecture
Apply robust security measures like HTTPS, SSL certificates, and secure authentication (such as multi-factor authentication) to protect user data and establish trust with your audience.
5. Analytics Integration
Use tools like Google Analytics or Hotjar to understand how visitors interact with your site. This insight helps you refine content, improve usability, and boost conversions over time.
Conclusion
This beginner’s guide to web development explores every essential step involved in building a modern, high performing website—from initial planning and intuitive design to development, deployment, and post-launch maintenance. A successful website is more than a digital presence; it’s a strategic business tool that supports growth, enhances user engagement, and adapts as your organization evolves. Each phase contributes to a smooth, secure, and scalable experience that meets user needs and business objectives alike.
Whether you’re launching your first website or giving an outdated one a much-needed refresh, collaborating with an experienced web development team can significantly impact the outcome. A skilled team brings technical precision, creative insight, and a user-focused approach to ensure your website is not only visually compelling but also functional, fast, and future-ready. With the right partner, your digital platform becomes a powerful asset that drives engagement, conversions, and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Web development is the process of designing, building, and maintaining websites or web applications, covering everything from visual layout and user interaction to server-side functionality and data management.
Development time depends on project scope. Simple websites can take 2–4 weeks, while complex, feature-rich platforms or web applications might require several months, including testing and deployment phases.
Front-end development focuses on the visual elements users interact with, while back-end development manages databases, servers, and application logic that run in the background to support functionality.
While no-code tools like WordPress simplify basic development, custom designs and advanced features still require coding knowledge in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or back-end languages like PHP or Python.
Yes, websites can be integrated with external systems such as CRMs, ERPs, and payment gateways using APIs, enabling automated data exchange and improved functionality for business operations.
To keep your site secure, implement SSL encryption, use secure logins, perform regular vulnerability testing, update software, and monitor for malware or suspicious activities to prevent cyber threats.
Websites should be updated regularly—at least monthly—for security patches, software upgrades, and content updates to maintain functionality, user experience, and alignment with SEO best practices.
Static websites show fixed content, ideal for simple projects, whereas dynamic websites use databases to deliver real-time content updates based on user interaction or server-side processing.
It simplifies complex concepts and walks you through planning, designing, coding, testing, and launching a site—making web development more approachable, especially for those with no technical background.
Essential tools include VS Code for coding, GitHub for version control, Chrome DevTools for debugging, and frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js to streamline front-end development workflows.
Yes, a reliable guide covers SEO basics like mobile responsiveness, fast loading speeds, semantic HTML, and metadata usage to help your site rank higher in search engine results.
Definitely. It includes tips and strategies for building feature-rich platforms, integrating shopping carts, payment systems, and dynamic product pages tailored for e-commerce and custom business needs.
Beginners guides are designed for all users. They start with foundational concepts, gradually introducing technical skills, allowing even those without coding experience to build functional and attractive websites.